In the hydrogen atom, the distance of electron from proton calculated on the basis of the Coulomb’s law
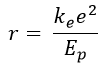
is 1.059 x 10-10 m.
Thus, we can calculate the force with which electron and proton attract each other in the hydrogen atom.
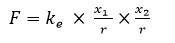
F – the attraction force between electron and proton,
x1, = e–, x2 = e+ – number of elementary charges in the hydrogen atom,
r – distance between the objects,
ke = 2,31 x 10-28 Nm2 – the electric constant,
Ep = 13,6 eV – the ionization energy
The force is
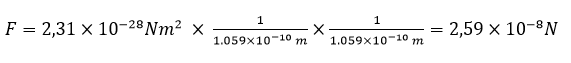
In the neutron, the distance of electron from proton is smaller than 1.059 x 10-10 m, but the exact value is still undetermined. Physicists have been concerned about this topic for years. There are a lot of theories in which this value is estimated at 10-21 – 10-34 m.
Let us then calculate the force with which charges in neutron will attract each other (according to the modern physics).
For the distance of 1 x 10-21 m the force will be
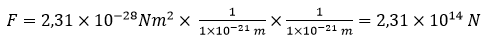
For the distance of 1 x 10–34 m the force will be
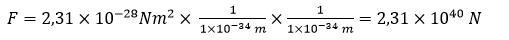
As it is apparent from the above, the physicists’ estimates are obviously overestimated; they are unreal. Neutron should be the most durable particle in the Universe. Neutron is durable only in an atomic nucleus. Having left the nucleus, it disintegrates almost immediately.

